
 Activities- These are performed tasks such as loops, various instances, and even subprocesses. Events – Sends a trigger to start such as receiving an alert or an issue warning. So then, you have several aspects that shape the model including: In addition, it helps to demonstrate how data and activities are combined to complete a process. Invariably, different components of a business are never completely independent.īPMN 2.0 helps to illustrate the connections to convey a clear perspective of how things work and where impacts can be made. Between swimlanes, you may find tasks and data. The swimlanes can be produced in multiples to represent every participant and their associated responsibility. Pools (May describe different departments or companies). Swimlanes (Resembling the lane lines of an Olympic swimming pool, these organize flow objects into varying categories). Connecting objects (Linked with flow objects to denote direction). Flow objects (Circles, rectangles, and diamonds which describe specific events or activities). To create a BPMN 2.0 diagram, a core set of elements are used and categorized into these three major groups: BPMN 2.0 can also be used to ensure that XML documents can be visualized using common notation.
Activities- These are performed tasks such as loops, various instances, and even subprocesses. Events – Sends a trigger to start such as receiving an alert or an issue warning. So then, you have several aspects that shape the model including: In addition, it helps to demonstrate how data and activities are combined to complete a process. Invariably, different components of a business are never completely independent.īPMN 2.0 helps to illustrate the connections to convey a clear perspective of how things work and where impacts can be made. Between swimlanes, you may find tasks and data. The swimlanes can be produced in multiples to represent every participant and their associated responsibility. Pools (May describe different departments or companies). Swimlanes (Resembling the lane lines of an Olympic swimming pool, these organize flow objects into varying categories). Connecting objects (Linked with flow objects to denote direction). Flow objects (Circles, rectangles, and diamonds which describe specific events or activities). To create a BPMN 2.0 diagram, a core set of elements are used and categorized into these three major groups: BPMN 2.0 can also be used to ensure that XML documents can be visualized using common notation. 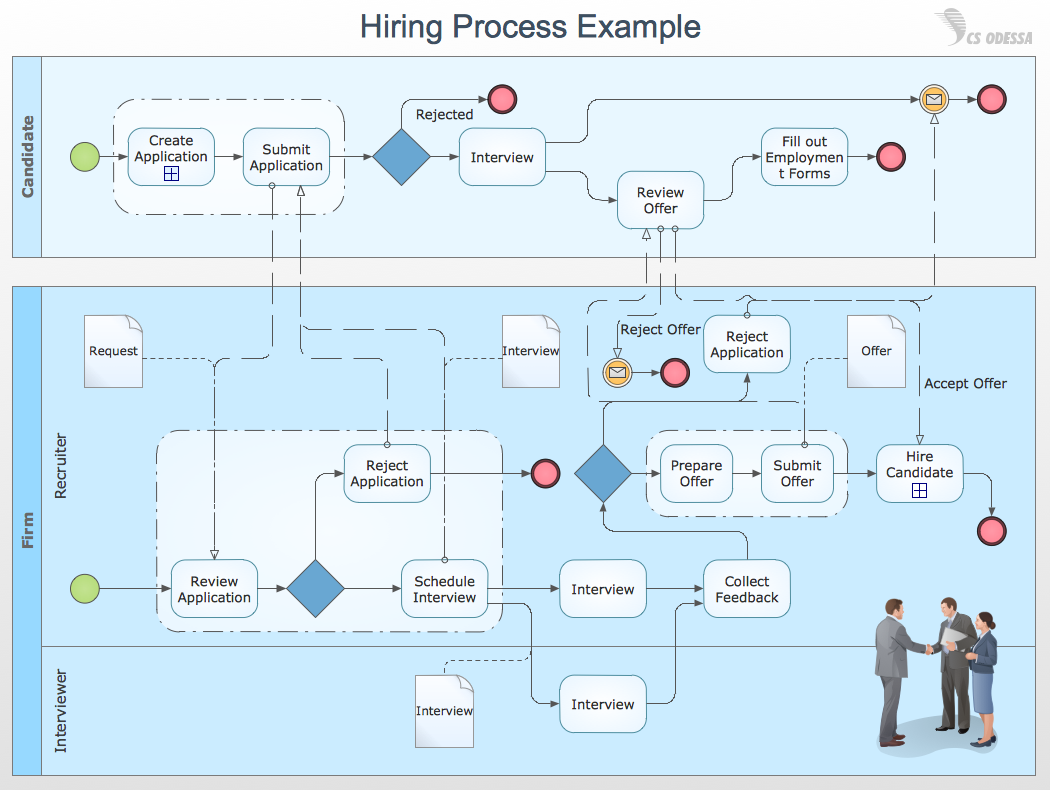
Further, it offers a standard notation that does not require elaborate training to comprehend. BPMN was initially created by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI). The diagram used shares some likenesses with a flow chart.
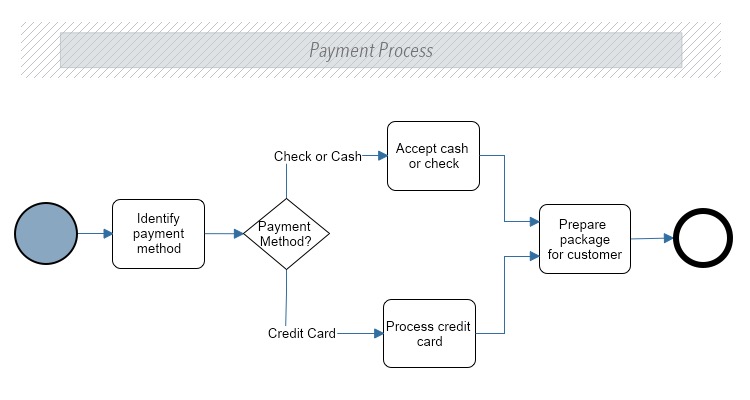
The objective of BPMN 2.0 is to use modeling for improvement in efficiency and to potentially garner a competitive advantage. Nonetheless, in environments that use process automation, BPMN 2.0 is significant in terms of value for helping participants to understand the process without extensive technical knowledge while also enabling purposeful troubleshooting before moving onto the next steps. In other cases, flow charts might be the visualization tool of choice. Part of the secret sauce lies within the utilization of standardized symbols.įrom the viewpoint of a business analyst, visual process models help to contextualize various processes so that every relevant stakeholder can understand. This article is part of a BPMN 2.0 tutorial, including uderstanding BPMN Symbols and Diagrams.īusiness Process Modeling and Notation 2.0 (BPMN 2.0) was designed to help remove the confusion from understanding process maps whether an employee or a consultant is trying to gauge the meaning.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
